Pavement Marking Design Manual
General Purpose of the Design Manual
Last Revised 6/20/19
This Pavement Marking Design Manual has been written to serve as a general guideline when designing pavement markings for the City of Overland Park, Kansas. Although there are specific design requirements, the guidelines contained herein should not be a substitute for proper engineering design and judgment based on specific situations. All pavement markings shall comply with the latest adopted edition of the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD). The purpose of this Pavement Marking Design Manual is to aid consultants as well as City of Overland Park staff to be consistent in the practice of designing pavement marking plans. It provides an overview of what tasks are expected to be included in the scope of the design; what information should be included on the plan sheets; what kind of backup design information is required; and what is expected for the final deliverable product. Any questions regarding this manual may be directed to Bruce Wacker, P.E., Assistant City Traffic Engineer at the City of Overland Park, Kansas at (913) 895-6027 or by email at [email protected].
Purpose of Pavement Marking:
Pavement marking provides guidance and information to the roadway user as well as supplement other traffic control devices such as signs, traffic signals and other markings. Pavement markings can convey regulations, guidance, or warnings.
Wherever applicable, this design manual should be used in conjunction with the latest adopted edition of the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) by the Federal Highway Administration. The current editions of the Design and Construction Standards, Volume 2 Construction Specifications (latest edition), the latest edition of the Standard Details and the Approved Materials List, hereafter referred to as “City Standards” should be followed during the design of all pavement marking plans.
Public or Private Ownership and Maintenance
Different policies apply to pavement marking based on the final ownership and maintenance. The two types of pavement markings are 1) those that are installed in the public right-of-way that will be owned and maintained by the City of Overland Park and 2) privately owned pavement markings that are installed on private property that will not be maintained by the City of Overland Park. Although each of the categories will be discussed, the design guidelines contained herein only apply to pavement markings that are within the public right-of-way or other City easements that are owned and maintained by the City of Overland Park.
City-Owned and Maintained Pavement Markings
All City-owned and maintained pavement markings shall be designed in accordance with the design criteria listed herein and use all pre-approved materials from the City’s Approved Materials List, which is available at City Hall or from the City’s web page. All pavement markings that are being designed in conjunction with the development of any public street or any developments that require modification of any pavement marking within the public right-of-way or other City easements by private consultants working for a developer are required to meet City Standards.
Privately Owned and Maintained Pavement Markings
A private street as defined, in City Resolution 4065, means a right-of-way which affords principal access to property abutting thereon, which right-of-way is owned, controlled and maintained by persons other than the public, which is named in accordance with the street name designated system on the City map and signed in accordance with Chapter 13.10 of the Overland Park Municipal Code. It is generally owned and maintained by a homes or business association or private citizens. The private streets are designated by a “Private Street” sign at the point of entry and typically have street name signs.
All pavement markings on private property are not required to be constructed using City approved materials. However, pavement markings on the approaches of a private street or drive that tie into City streets shall be designed to conform to these guidelines and the MUTCD. The City may make requests to the owners to maintain private pavement markings from time to time in order to improve visibility, reduce driver confusion, or to coordinate with lane use changes that would affect the traveling public in conjunction with the lane use on adjacent public roadways.
Functional Roadway Classifications
The following pavement marking design criteria will be used for all thoroughfare roadways, super collector roadways, collector roadways and residential roadways as identified on the latest edition of the City of Overland Park “Official Street Map” available from the Planning and Development Services Department.
Thoroughfare Roadway
The thoroughfare roadway classification includes all thoroughfare roadways whether divided or undivided; whether improved or unimproved; and whether two-lane, four-lane or six-lane excluding auxiliary left and right turn lanes; regardless of the volume of traffic.
Collector Roadway
The collector roadway classification includes all super-collector and collector roadways regardless of the number of lanes; whether improved or unimproved; regardless of the volume of traffic.
Residential Roadway
The residential roadway classification includes all local residential and cul-de-sac roadways; whether improved or unimproved; regardless of the volume of traffic.
Colors of Markings
Markings shall be either white or yellow and conform to the standard highway colors.
White Pavement Markings
White markings, when used for longitudinal lines shall delineate the separation of traffic flows in the same direction or the right-hand edge of the roadway. White markings shall also be used for crosswalk lines, stop lines and pavement marking symbols, with the exception of the symbol of accessibility and interstate route shields, etc.
Yellow Pavement Markings
Yellow markings, when used for longitudinal lines shall delineate the separation of traffic traveling in opposite directions; the left-hand edge of the roadway or divided street or one-way streets; and the separation of two-way left turn lanes.
Function, Widths and Classifications of Pavement Markings
There are several different types of pavement markings applicable to specific situations. The City of Overland Park has specific design considerations that should be reviewed for each type of pavement marking.
Function
- A double line indicates maximum or special restrictions and does not allow any crossing of the line.
- A single solid line discourages crossing.
- A broken line indicates a permissive condition
- A dotted line provides guidance or warning of a downstream change in lane function.
Widths and Patterns
- A normal width line is 4”.
- A wide line is twice the width of a normal line, or 8”.
- A double line consists of two parallel lines separated by a 4” space (measured from edge of line to edge of line).
- A broken line consists of a normal line segment separated by gaps.
- A dotted line is a noticeably shorter line segment separated by shorter gaps than used for a broken line. The width of a dotted line extension shall be the same width of the line it extends.
Classification of Markings
Markings are either classified as longitudinal, transverse, or symbols.
Longitudinal Markings
These are lines that generally run parallel to the direction of traffic and include:
- Solid double centerlines
- Broken centerlines
- Solid and broken centerlines
- Broken lane lines
- Solid lane lines
- Broken lane extension lines
- Edge lines
- Solid lane lines
- Lane drop lines
- Bicycle lane lines, etc.
Transverse Markings
These are lines that generally run perpendicular to or at an angle to the direction of traffic and include:
- Diagonal crosshatch lines
- Chevrons
- Stop lines
- Crosswalk lines
- Roundabout extension edge lines
- Perpendicular or angled parking space lines, etc.
Symbol Markings
Symbol markings are all other markings that are not considered “lines” but consist of geometric shapes or words. They include:
- Yield lines
- Turn arrows, thru arrows, or combination arrows
- Merge arrows
- Railroad crossing markings
- ONLY markings
- Bicycle lane symbols
- Bicycle lane arrows
- Sharrow markings
- International symbol of accessibility, etc.

|
Top | General Purpose |
Yellow Centerline Markings
Yellow centerline markings are used to delineate the separation of traffic lanes that have opposite directions of travel. They are used on thoroughfare roadways, collector roadways, and super collector roadways regardless of the posted speed. Centerline markings are not installed on residential roadways except in specific situations in advance of intersections as addressed below.
The yellow centerline markings, whether broken or solid double lines, should be continuous through residential drive entrances and alleys but should break at intersections with public streets and private streets as defined above. Breaks in the centerline should not be made at single family or multi-family drive entrances. They should also not be broken at intersections with commercial drive entrances unless the main roadway has left or right turn lanes accessing the site or the intersection with the commercial drive is controlled by a traffic signal.
At breaks in the centerline, the beginning and end of the centerline should be evaluated based on the left turn movement of the design vehicle from the side street. The beginning or end of the line should be at the point where the design vehicle does not drive over the line while making a left turn. This should be determined using turning movement templates for the specific design vehicle.
Centerlines on Residential Streets
Centerlines are not typically installed on residential streets. However, the following conditions would warrant centerline markings near intersections with other streets:
- When a residential street has more than one approach lane to an intersection that is marked with solid white lane markings, a double yellow centerline should be installed in advance of the stop line for a minimum of 50’ or for the length of the solid white lane markings.
- At a multi-way stop-controlled intersection between two residential streets, a solid double yellow centerline shall be installed starting a minimum of 50’ in advance of the stop line on all approaches.
Centerlines on Collector Streets
All two-lane collector streets, regardless of width, shall be striped with a centerline consisting of a 4” wide broken yellow line with a 6’ stripe and an 18’ gap (3:1 ratio). Collector streets that consist of more than two lanes shall be striped with a 4" solid double yellow centerline.
See the section on Transitions from Broken Yellow Centerlines below for treatment of centerlines at intersections.
Centerlines on Apartment Streets
Apartment streets that are 36’ wide (measured from back of curb to back of curb), that have a posted speed limit of 30 mph, shall have a marked centerline consisting of a 4” wide broken yellow line with a 6’ stripe and an 18’ gap (3:1 ratio).
See the section on Transitions from Broken Yellow Centerlines below for treatment of centerlines at intersections.
Centerlines on Commercial and Industrial Streets
Commercial streets or industrial streets may range in width from 36’ to 52’ (measured from back of curb to back of curb) to accommodate left or right turn lanes or additional through lanes for added vehicle capacity. Centerlines should consist of 4” wide broken yellow lines with a 6’ stripe and an 18’ gap (3:1 ratio) or 4” solid double yellow lines depending on the number of lanes. Broken yellow centerlines would be used where there are no auxiliary lanes such as right or left turn lanes. Double yellow centerlines should be used at multi-lane cross-sections and may terminate at an intersection with a painted median. Depending on the number of access points, a two-way left turn lane may be provided as approved by the City Engineer. Painted medians and Two-way left turn lanes are discussed below.
See the section on Transitions from Broken Yellow Centerlines below for treatment of centerlines at intersections.
Centerlines on Super-Collector Roadways
Super-collector roadways range from two undivided through lanes that are 36’ wide (back of curb to back of curb), to divided roadways with four through lanes. Centerline pavement markings should either be 4” wide broken yellow line with a 6’ stripe and an 18’ gap (3:1 ratio) or 4” solid double yellow lines depending on the number of lanes. Broken yellow centerlines would be used on two-lane super-collector streets where there are no auxiliary lanes such as right or left turn lanes, while double yellow centerlines should be used at multi-lane cross-sections. Proper transitions between broken centerlines and painted or raised medians should be provided as discussed in Transitions from Broken Yellow Centerlines below. Depending on the number of access points, a two-way left turn lane may be provided as approved by the City Engineer. Two-way left turn lanes are discussed below.
Centerlines on Thoroughfare Roadways
The following guidelines are established for centerline pavement markings on thoroughfare roadways, consisting of divided or undivided roadways and improved or unimproved roadways. Undivided thoroughfare roadways fall into two categories: 1) unimproved and 2) improved.
Unimproved thoroughfares have two through lanes of traffic that have not been widened. These primarily exist in the southern portions of the City that have been taken over from the County through annexation and where development has not fully occurred to require the roadway to be widened due to increased traffic volumes.
Improved thoroughfares have been widened to provide for at least two lanes of through traffic with shoulders or four to six lanes of through traffic with curb and gutter sections. The two-lane, four-lane or six-lane thoroughfares may be divided or undivided.
Centerlines on Divided Thoroughfare Roadways
Divided thoroughfare roadways that have a continuous median, except for breaks at approved intersections, do not require centerline pavement markings if the center median consists of raised curbs. When the center median is depressed, the centerline pavement marking should consist of a single 4” solid yellow edge line on each side of the depressed median. The yellow edge line should be installed 4” from the edge of the driving surface to the closest edge of the line.
Thoroughfares with intermittent raised medians shall have a 4” solid double yellow centerline in those sections that do not have a center median. Any time a raised median section is provided, centerline markings are not required. Proper transitions between broken centerlines and painted or raised medians should be provided as discussed in Transitions from Broken Yellow Centerlines below.
Centerlines on Undivided, Improved Thoroughfare Roadways
Undivided, improved thoroughfare roadways should consist of 4” solid double yellow centerlines. Depending on the number of access points, a two-way left turn lane may be provided as approved by the City Engineer. Two-way left turn lanes are discussed below.
Centerlines on Undivided, Unimproved Thoroughfare Roadways
Undivided, unimproved thoroughfare roadways should always consist of 4” solid double yellow centerlines. Passing is prohibited on these types of roadways.
Transitions from Normal Centerlines
Transitions often occur from the normally used centerline approaching intersections or raised medians. This can occur with either broken yellow centerlines or double yellow centerlines. The following discussion provides guidance in the design in various applications.
Prior to Raised Medians
When transitioning from a broken yellow centerline to a raised median, the raised median should be preceded by a double yellow centerline a minimum of 100’ in length unless there is some engineering reason that limits it to less than 100’, e.g. another intersection. This length should be increased if it places the beginning of the double yellow centerline near the blind side of a crest vertical curve.

|
| Centerline Transition at Raised Median |
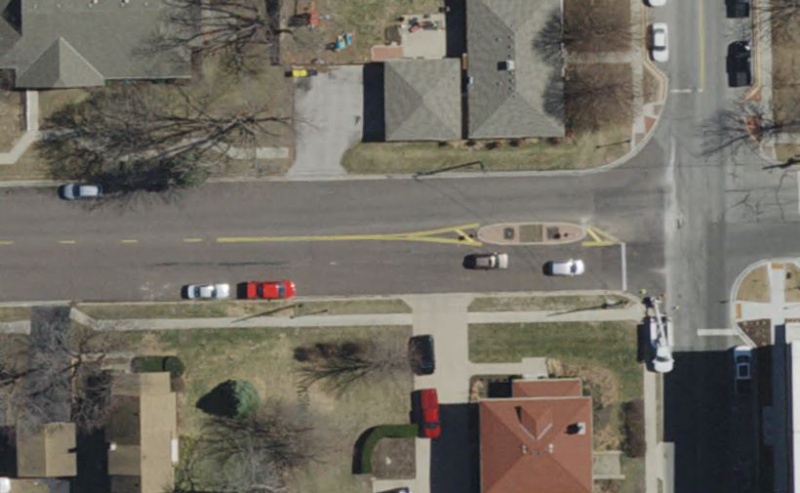
When transitioning from a double yellow centerline to a raised median, the double yellow line should end near the raised nose of the median in order to provide a smooth transition directing traffic away from the median. When the median width, at the widest part, is greater than 6' (measured from the back of curbs), the double yellow centerline should be marked for approaching as well as for departing vehicles.
When the median width, at the widest part, is less than 6' (measured from the back of curbs), the double yellow centerline should be marked for approaching traffic only.
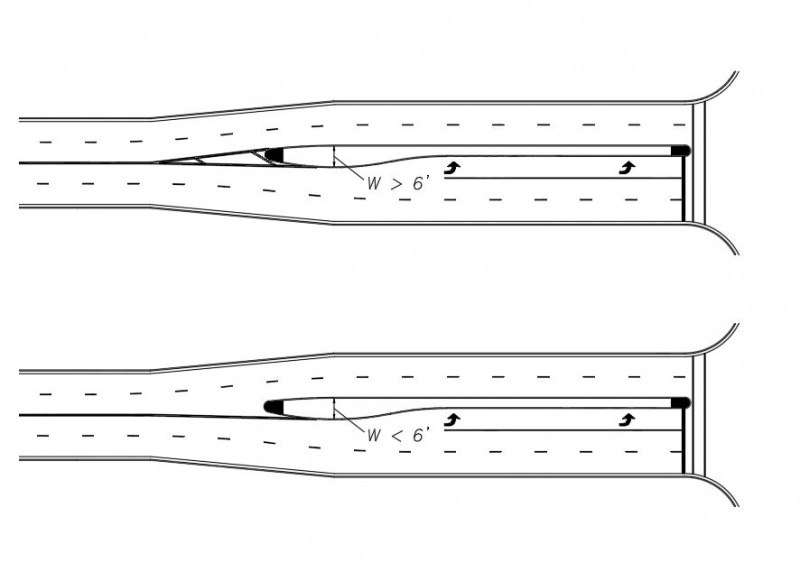
|
| Centerline Transition at Raised Median Based on Width |
Prior to Painted Medians
When transitioning from a broken yellow centerline to a painted median, the painted median should be preceded by a double yellow centerline a minimum of 100’ in length unless there is some engineering reason that limits it to less than 100’, e.g. another intersection. This length should be increased if it places the beginning of the double yellow centerline near the blind side of a crest vertical curve.
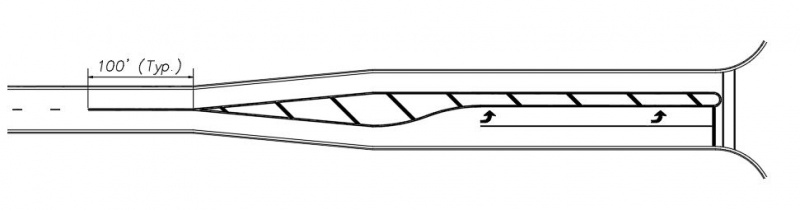
|
| Centerline Transition at Painted Median |
Prior to Stop Controlled Intersections
A broken yellow centerline should transition to a double yellow centerline a minimum of 100’ prior to the stop line (or designated stopping point in the absence of a stop line) at an intersection controlled by a stop sign.
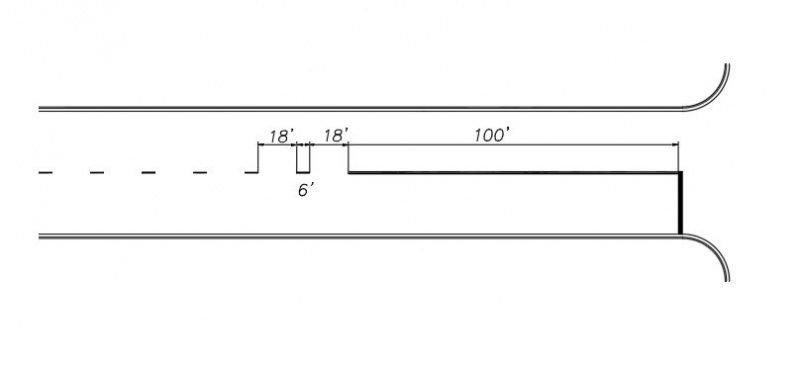
|
| Broken Centerline Transition at Stop Controlled Intersection |
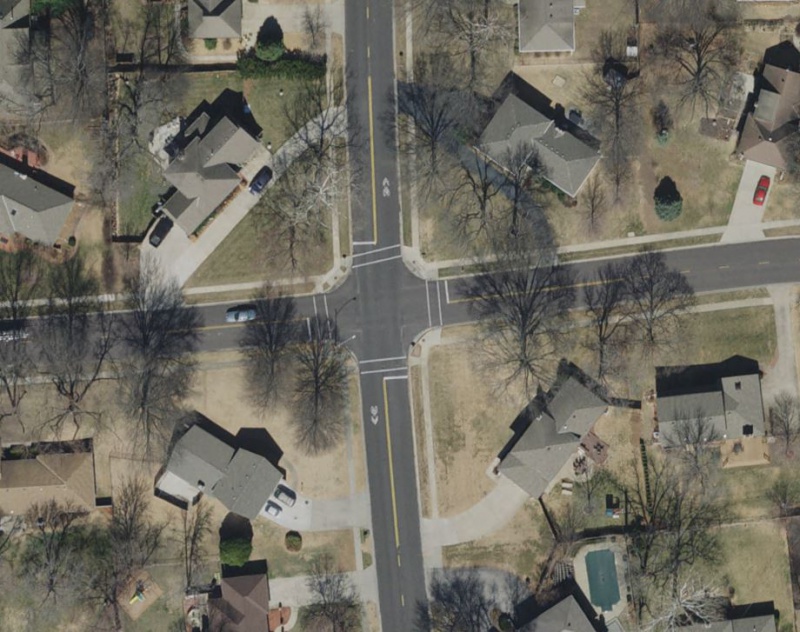

|
| Four-Way Stop at Collector-Collector Intersection |
Special Situations at Intersections
Occasionally, a collector street will turn into a residential street at a two-way stop controlled intersection with another through street segment. The minor collector street leg, which is controlled by a stop sign, will be striped with a broken yellow centerline that transitions to a double yellow centerline 100’ in advance of the stop line. The residential street leg, which is controlled by a stop sign, will not require either a stop line or a centerline.
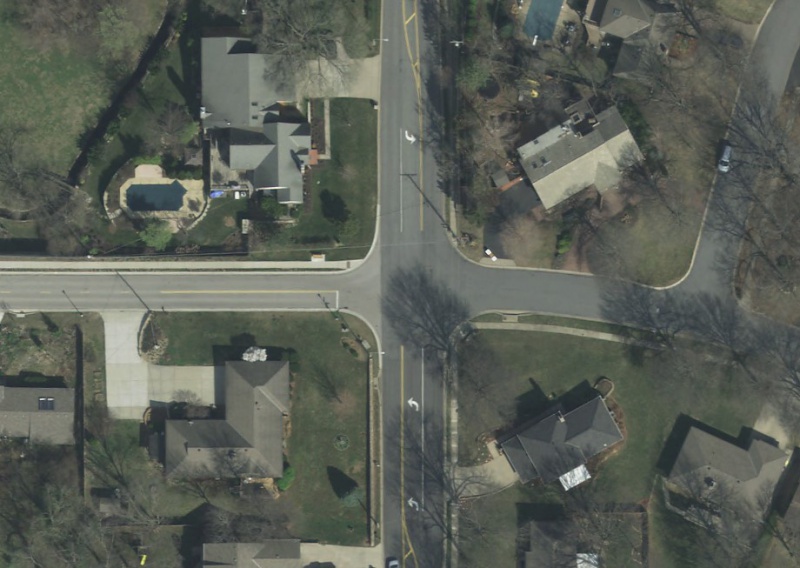

|
| Special Situations at Intersections |
Painted Medians
Painted medians should be used on undivided roadways where it is desirable to provide left turn lanes or separate traffic traveling in opposite directions. For left turn lanes, it is preferable to provide a complete approach taper and a fully shadowed bay taper whenever possible and pavement width permits.
Painted medians also occur in advance of a raised median that has been installed for access control near an intersection approach or in advance of a splitter island of a roundabout. Painted medians should consist of 4” solid double yellow lines with 12” yellow diagonal crosshatch lines. See Yellow Diagonal Crosshatch Lines for more information.
Yellow Solid and Broken Lane Lines
No-Passing Zone Lines
Yellow solid and broken lane lines can be used where crossing the center line markings for passing is permitted for the traffic traveling adjacent to the broken line, but is prohibited for traffic traveling adjacent to the solid line. This centerline marking is typically not used in the City of Overland Park. It requires a passing sight distance study in order to determine where passing is permitted.
Two-way Left Turn Lanes (TWLTL)
Two-way left turn lanes (TWLTL) should consist of 4” solid yellow lines on each side of the travel lane with six foot long 4” broken yellow lines inset inside of the solid yellow lines with 18’ long gaps. The beginning and end of the broken yellow lines should line up with any adjacent broken white lane lines.
The TWLTL should terminate into a left turn lane. There should be a 42’ long gap between the end of the broken and solid yellow line and the beginning of the 4” solid white lane line for the left turn storage. Two sets of white left turn arrows should be placed 25’ apart measured from the tails of both arrows. The spacing of the arrow sets is dependent on the overall length of the TWLTL. Generally, one set is installed 30’ from the beginning, one set 30’ from the end and one set at approximately the midpoint, but the distance between sets of arrows should not exceed 160’.
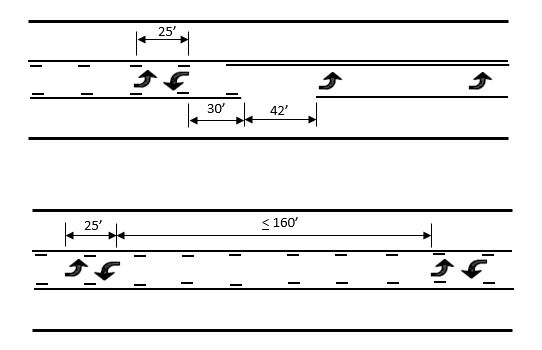
|
| Two-way Left Turn Lanes |

|
Top | Yellow Centerline Markings |
Broken White Lane Lines
Broken white lane line markings should be used on all roadways with two or more adjacent traffic lanes that have the same direction of travel. They shall consist of a 4” wide broken white line with a 6’ stripe and an 18’ gap (3:1 ratio).
The beginning point of broken white lane lines between adjacent lanes of travel on a multi-lane street should line up with each other.
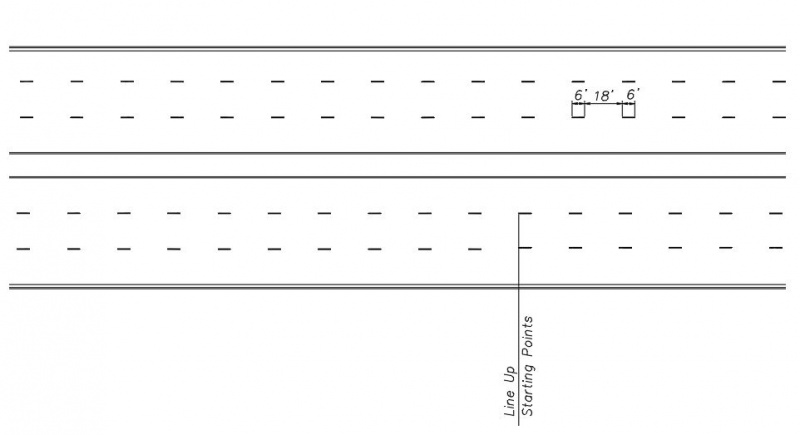
|
| Alignment of Adjacent Broken White Lane Lines |
Ideally, the beginning of a broken white lane line should also line up with the beginning of any adjacent solid white lane line delineating the storage length for a right or left turn lane. However, broken white lane lines should not extend past the stop line.

|
| Alignment of Broken White Lane Line with Solid White Turn Lane Line |
Broken white lane lines should break on each side of a four-legged intersection, comprised of public streets, allowing side street traffic to cross without running over the lines. Broken white lane lines should extend through intersections with private and commercial driveways. However, if the main street has a left turn lane into the commercial drive of the development, lane lines should not be marked through the intersection. It would be treated like a standard intersection with public streets.
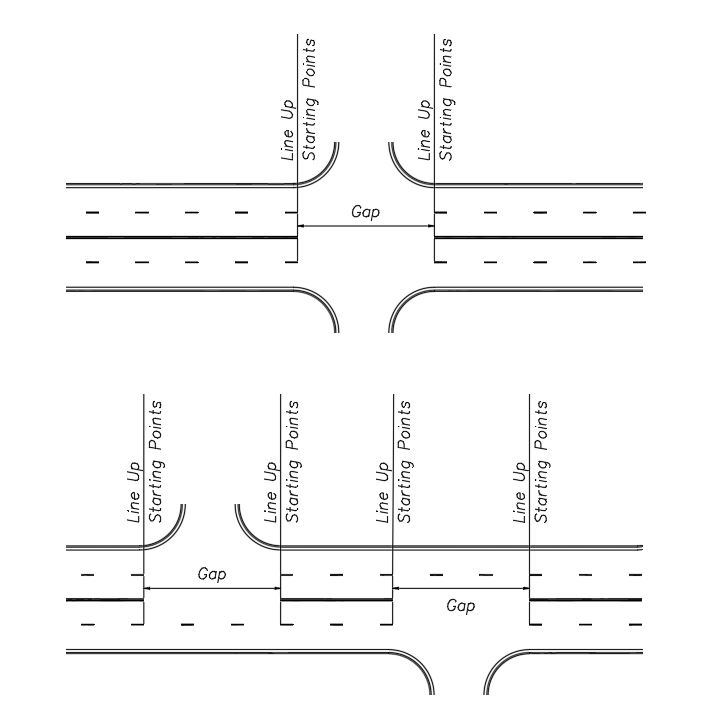
|
| Gaps in Broken White Lane Lines at Intersections |
At tee intersections, the broken white lane lines will continue through the intersection at the top of the tee, but will not extend through the intersection with the lanes closest to the intersecting side street.

|
Top | Broken White Lane Lines |
Broken White Lane Extension Lines
Broken white lane extension lines are used for guiding the traveling public through more complex roadway lane configurations such as:
- Offset through lanes
- Skewed intersections
- Curved roadways
- Where multiple turn lanes are present
- At interchanges where there are extended left turn lanes on the thoroughfare street
- Roundabout circulating lanes
- Where accident history indicates a presence of sideswipe type crashes
The broken white extension line shall be 4” wide and 2’ long with a 4’ gap.
Offset Through Lanes
Depending on the roadway classification and the posted speed, offset through lanes can create situations where white lane extension lines would be beneficial to delineate the travel path of vehicles. Offsets through intersections on a thoroughfare are generally more of a concern than offset through lanes on a collector roadway or a local street. The following gives some guidance on when to install lane extension lines for offset through lanes, but the designer in conjunction with City staff, should use engineering judgment to make the final determination whether to use them or not. Having multiple lines crossing through an intersection can be just as confusing as not having any. Discretion should be used keeping in mind the long term aspects of maintenance, since pavement markings in an intersection are worn down frequently by traveling vehicles.
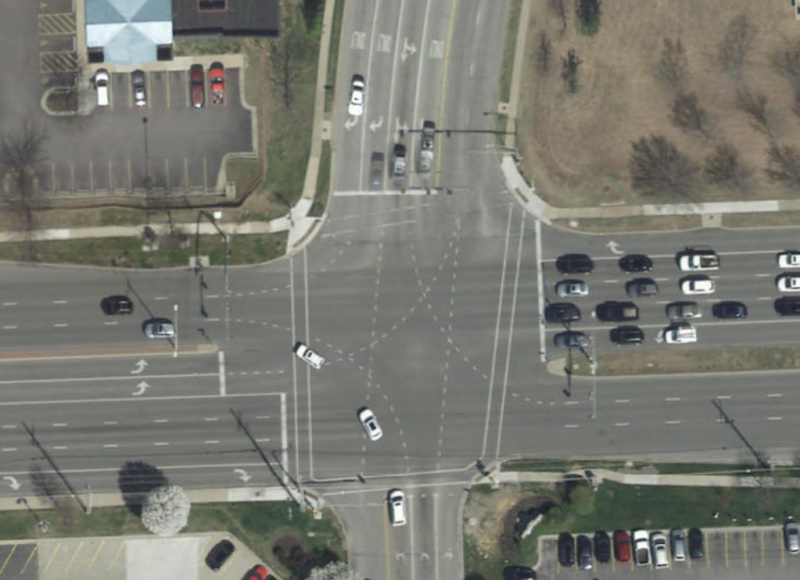

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Lines at Intersections |
When the through traffic lanes on a thoroughfare across an intersection are offset at least one fourth of the width of the lane, white lane extension lines should be considered, especially if the presence of a crest vertical curve near the center of the intersection obstructs the view of the receiving lanes on the opposite side of the intersection. When the offset is one half or more of the width of the lane, the extension lines shall be installed.

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Lines Through Intersections |
Skewed Intersections
At skewed intersections, where there is a possibility for the opposing turning traffic to overlap paths, white lane extension lines should be considered to delineate the paths regardless of the number of turn lanes or the number of receiving through lanes.
Curved Roadways
Where a vehicle, following a curving curb line, could drift into a left turn or right turn lane, a white extension line should be considered to delineate the path of the vehicle.

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Lines on Curved Roadway |
Multiple Left or Right Turn Lanes
Broken white lane extension lines are not typically used where the number of turn lanes on the side street is equivalent to the number of receiving through lanes on the major street. For example if two left turn lanes are turning into two through lanes.
They shall be used within an intersection where there are two left turn or two right turn lanes but three or more receiving through lanes. They shall also be used anywhere the number of left turning lanes or right turning lanes is greater than two, regardless of the number of through lanes available for receiving lanes. For example, if a side street has two exclusive left turn lanes and one shared through/left turn lane, the white extension lines shall be installed directing traffic into their respective lanes, even if there are only three through lanes on the main street.
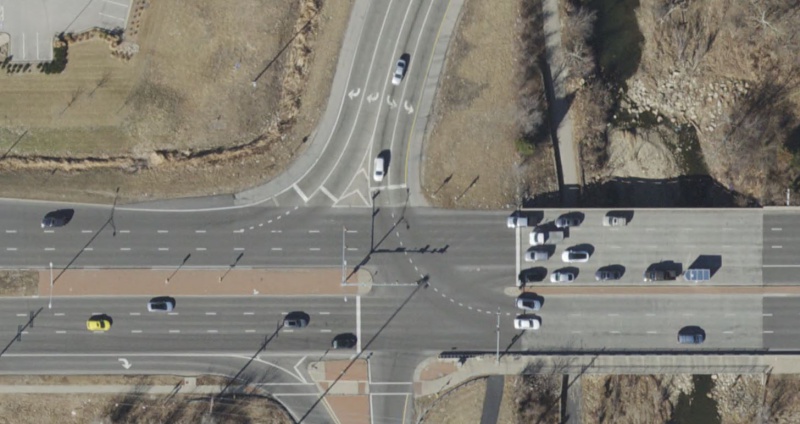

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Line at Multiple Turn Lanes |
At Interchanges with Extended Left Turn Lanes on the Thoroughfare
There are occasions, primarily at interchanges with thoroughfare streets, where there are only two through lanes but the left turn lanes extend upstream of the intersection to increase the storage length. Even though there are only single or dual left turn lanes coming off the ramp and only two receiving through lanes, the broken white lane extension lines should be installed for the ramp traffic so vehicles do not get trapped into the left turn lanes on the thoroughfare.
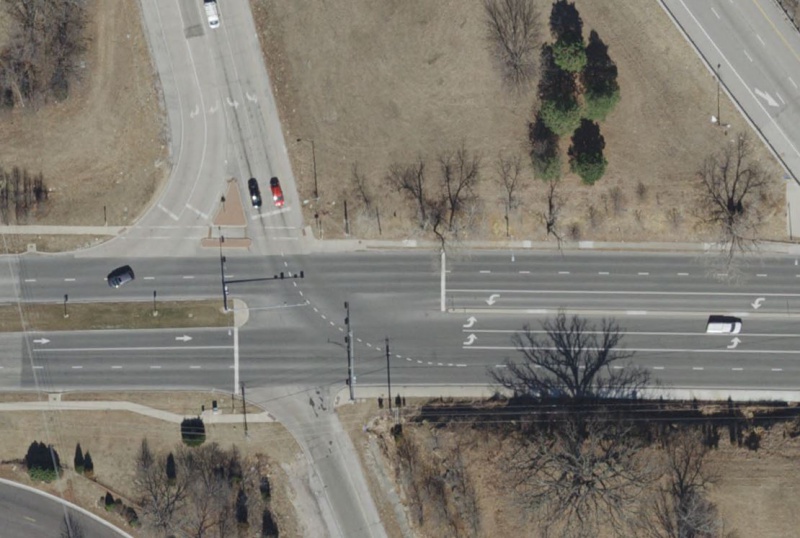

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Line at Interchanges with Extended Left Turn Lanes |
Roundabout Circulating Lanes
Lane extension lines should be installed in the circulating lanes at multi-lane roundabouts opposite the points where lanes from the intersecting roadways enter the roundabout. They should extend toward the exit lanes to direct circulating traffic that is exiting the roundabout to the correct receiving lanes.
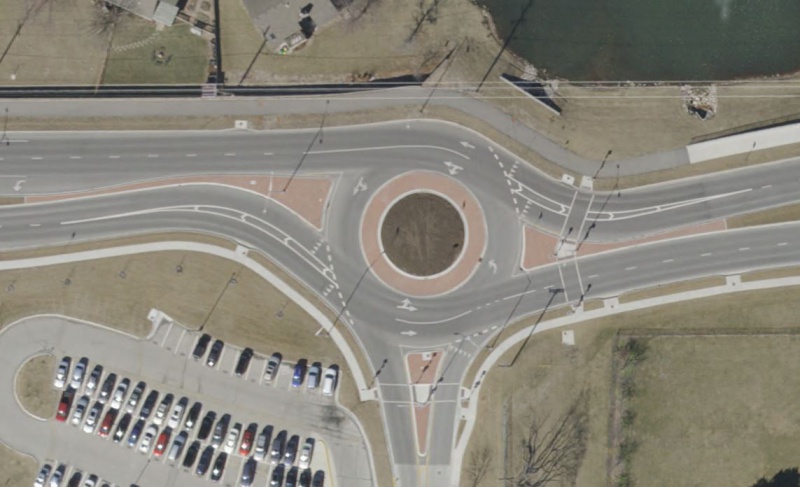

|
| Broken White Lane Extension Line at Roundabouts |
Where Accident Crash History Shows a Need
Lane extension lines should be installed where there is a history of side swipe crashes that could be alleviated by providing more guidance to the driver.

|
Top | Broken White Lane Extension Lines |
Wide Dotted Line
A wide dotted white line marking shall be used as the lane line to separate a through lane that continues beyond the intersection from an adjacent lane that becomes a mandatory turn lane or across the lane(s) entering a roundabout as follows:
Wide Dotted Lane Drop Line
Wide dotted lane drop lines are used for lane drops (trap lanes) where an otherwise through traffic lane turns into a mandatory left turn or right turn lane. Where used, the wide dotted lane drop line shall be 8” wide with a 3’ line segment and a 9’ gap. The wide dotted lane drop line will be accompanied by a 8” wide white solid lane line beginning at the downstream end of the white dotted lane drop line to the stop bar (See White Solid Wide Lane Lines). The length of the dotted lane drop shall be as follows:
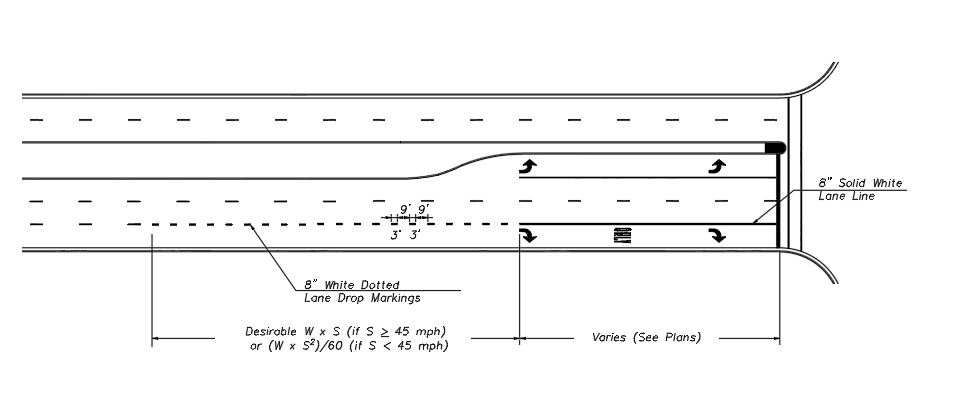
|
| Typical Wide Dotted Lane Drop Lines |

|
| White Dotted Lane Drop Lines with No Restrictions |
Length Based on Posted Speed Limit
For posted speed limits > 45 mph, the length of the wide dotted lane line shall be based on the merge length equation: L = W x S, where W is the width of the lane and S is the posted speed limit, (mph). For posted speed limits < 45 mph, the length of the wide dotted lane line shall be based on the merge length equation L = (W x S2)/60. Exceptions to this rule are as follows:
Spacing Considerations for Closely Spaced Intersections
If the calculated length of the wide dotted lane drop line would extend it into or through an upstream four-legged intersection (whether controlled or uncontrolled), it should begin immediately past the upstream intersection instead of using the full calculated length. The lane drop line should begin no closer to the intersection than the most upstream regulatory or warning sign associated with the lane drop. An R3-7 (R or L) sign should be installed approximately 30’ from the curb return at the upstream intersection. If the posted speed limit is > 35 mph, an additional R3-7 (R or L) should be installed at the beginning of the 8" solid wide lane line. If the posted speed limit is < 35 mph, no additional sign is needed at the beginning of the 8" solid wide lane line.
The calculated length of the wide dotted lane drop line can extend through a three-legged T-intersection as long as the major street that has the trap lane is divided with a median. In that case, an R3-7R sign will be installed at the beginning of the wide dotted lane drop line with a street name sign plaque mounted underneath to designate where the lane drops.

|
| Wide Dotted Lane Drop Lines Thru T-Intersection |
In areas where there is not enough room to achieve the full length without extending through an intersection, a balance should be maintained between the lane drop line and the required storage bay length, based on the observed traffic volumes.
Wide Dotted Lines at Roundabouts
White wide dotted lines should be used across the lane(s) entering a roundabout to mark an extension of the circulatory roadway edge line. They should extend from the splitter island to the exit of the roundabout and be a three foot long, 12” wide line with a three foot gap.
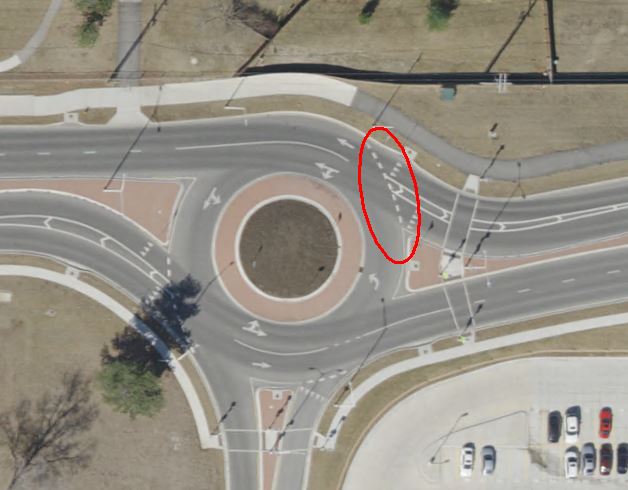

|
| Wide Dotted Roundabout Line |

|
Top | Wide Dotted Line |
Solid White Lane Lines
Solid white lane lines are used where drivers are discouraged from changing lanes. The lane line markings shall consist of a 4” wide solid white line. Solid white lane lines are typically used at intersections to separate a through lane from a mandatory left or right turn lane.
Single Left or Right Turn Lanes
The solid white lane line should extend from the stop line upstream to where the full width of the turn lane begins.
Dual Left or Right Turn Lanes
In the case of dual left or right turn lanes, the inside line should begin at the point of tangency with the median curb, where the full width of the inside lane is available. The outside line should be extended farther upstream to where the lane opening, measured perpendicular from the median curb to the start of the line is 18’, as shown below.
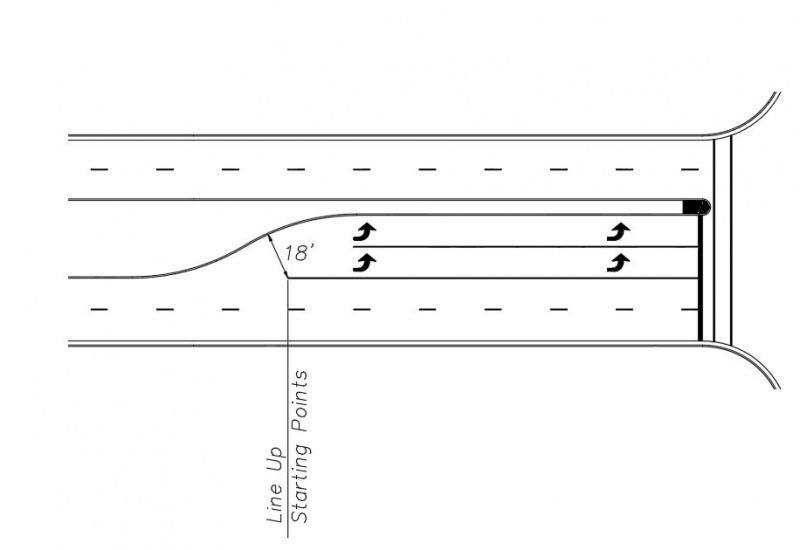
|
| Solid White Lane Lines for Dual Left Turn Lanes |
Continuous Right Turn Lane Exceptions
Where a right turn lane at an intersection would have one or more driveway entrances within the storage bay, the preferred approach is to break the solid white lane line for the driveway and treat them as separate turn lanes. An R3-7(R) sign should be installed at the driveway.
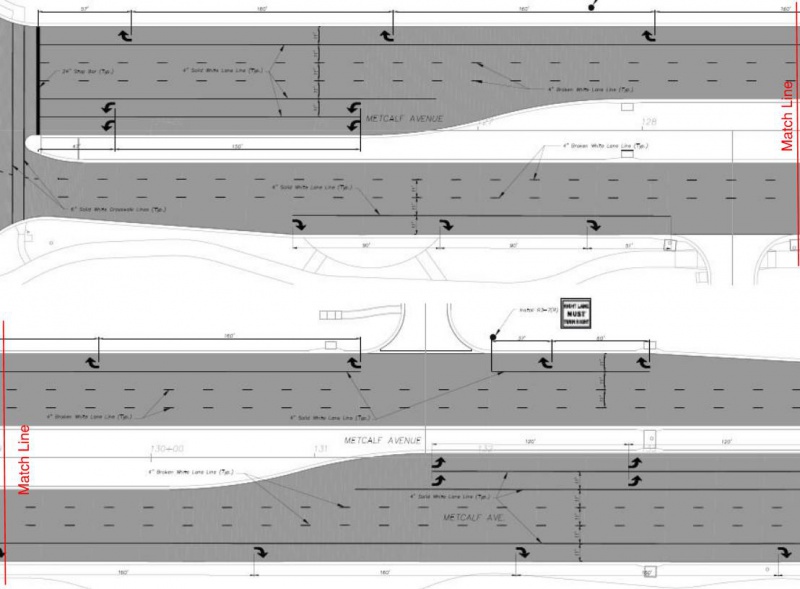
|
| Solid White Lane Lines for Continuous Right Turn Lanes |
If a driveway is located near a signalized intersection such that the distance between the driveway and the intersection does not provide enough storage length, then the solid lane line should be continued through the driveway.
If a driveway occurs at a median break, the lane line should not be carried through the intersection. In the example below, the lane line was continued through the first driveway because the right turn lane was just beginning and not enough storage length was available for the driveway. The R3-7(R) sign was removed for the driveway.
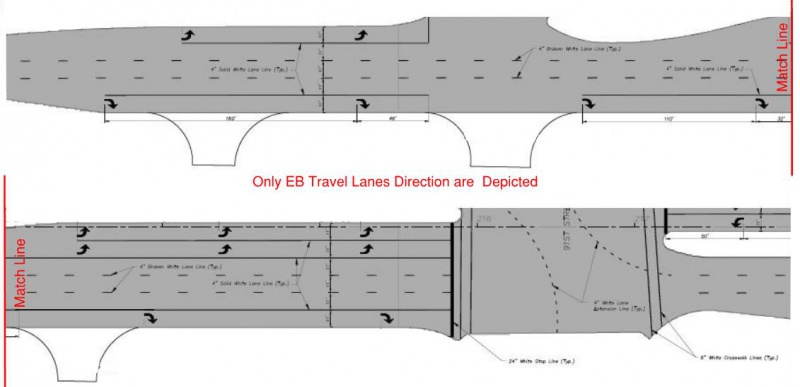
|
| Solid White Lane Line Exception for Continuous Right Turn Lanes |

|
Top | Solid White Lane Lines |
Solid Double White Lane Lines
Solid double white lane lines are used to mark where crossing is prohibited or whenever two lanes of traffic, traveling in the same direction, are separated by a painted median. The most common instance of this occurs between a turn lane and a through lane which is separated by a painted island. This normally occurs when an intersection has offset left turn lanes that are separated from the through lanes to give drivers on opposing approaches a less obstructed view of opposing through traffic. They are also used when an intersection is designed for ultimate double left turn lanes, but one lane has been marked out until sometime in the future when it is required based on traffic volumes. The lane line markings shall consist of a 4” wide solid double white lines separated by a 4” space. White 12” chevron should be installed between the two sets of solid double white lane lines. (See White Chevrons) for more information in regard to spacing.
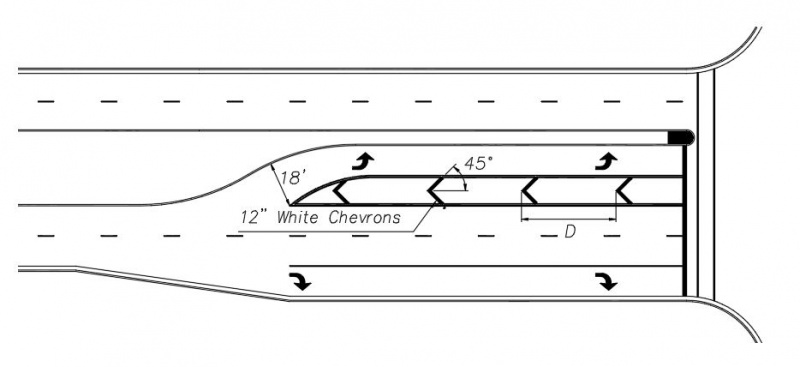
|
| Solid Double White Lane Lines |
White Solid Wide Lane Lines
Solid wide channelization lines are used to form islands where traffic traveling in the same direction is permitted on both sides of the island. They should be 8” wide and used to outline around painted or raised medians as follows:
At Interchange Ramps
Channelizing lines at entrance ramps define the neutral area, directing exiting traffic at the proper angle for smooth divergence onto the ramp. They should be used to outline raised islands or used for painted islands that separate interstate ramp movements from through movements on thoroughfare streets.
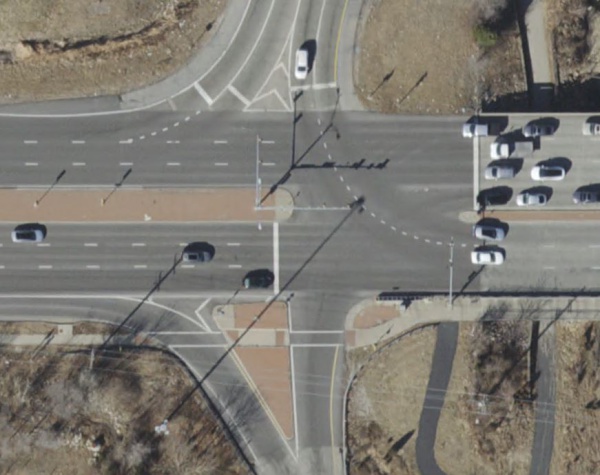

|
| White Solid Wide Lane Lines at Interstate Ramp Islands |
At Free Flow Right Turn Lanes
They should also be used to outline the raised medians for free flow right turn lanes on City streets.
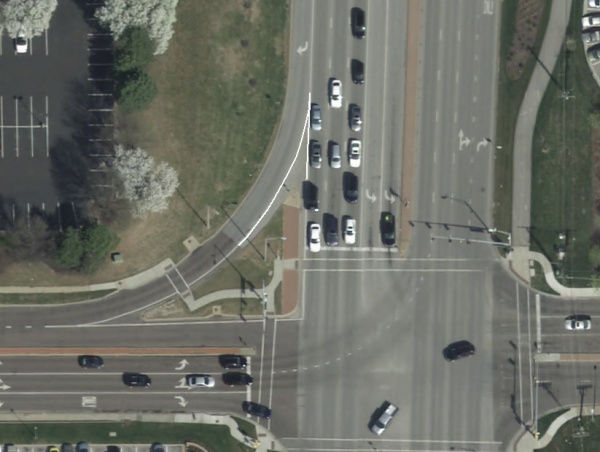

|
| White Solid Wide Lane Lines Around Islands at Intersections |

|
Top | White Solid Wide Lane Lines |
White Edge Lines
Edge lines are 4” wide lines that are used to delineate the right or left edges of roadways that have paved or turf shoulders. If they are on the left hand side of the roadway, they shall be yellow. They shall be white if they are on the right hand side of the roadway. Edge lines shall not be continued through intersections or major driveways that consist of turn lanes entering from the major street. But they would extend through minor driveways. They should be placed on rural thoroughfares and collectors with a traveled way of 20’ or more and an average daily traffic (ADT) of 3,000 vehicles per day or greater. If a bicycle lanes is marked on the outside portion of the traveled way, the edge line that would mark the outside edge of the bicycle lane should be omitted.
In the case of turf shoulders, the edge line shall be inset to allow a minimum of 4” from the edge of the asphalt roadway to the edge of the line.
Edge Lines on Diverging Diamond Interchanges (DDI’s)
Edge lines on diverging diamond interchanges (DDI’s) require clarification. The two directions of travel are separated by either a raised median or bridge rails. This would normally require the edge line separating the two directions of travel to be yellow. However, this violates the rule that yellow lines shall always be on the left hand side of the driver. Therefore, the pavement for the two directions of travel are treated as separate, one-way roadways. Therefore, the edge lines will be yellow on the left side and white on the right side for drivers traveling in each direction.
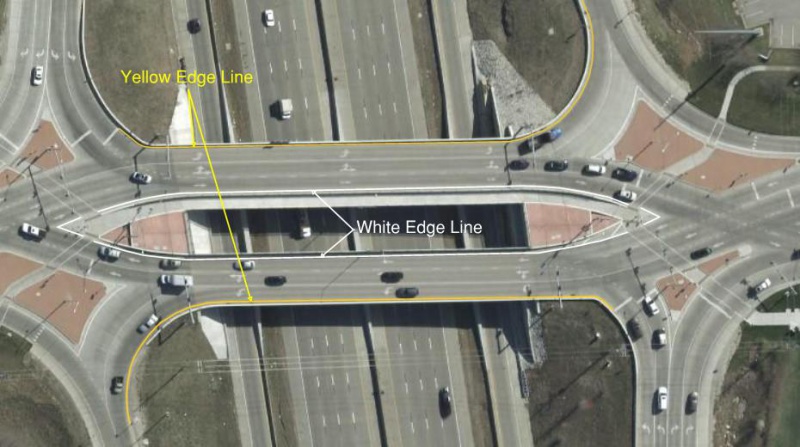
|
| Edge Lines for Diverging Diamond Interchanges (DDI's) |
Edge Lines on Bridges
Edge lines should be installed across all bridges, regardless of whether the roadway approaches to the bridge consist of curb and gutter or shoulders. The edge line should be offset from the bridge rail to provide a horizontal buffer space for vehicles and to maintain a constant lane width across the bridge.
